Social Security Benefits: A Beginner’s Guide to understand
Social Security benefits are crucial for many Americans. They provide financial support during retirement, disability, or after the loss of a loved one.
Understanding Social Security benefits can be a game-changer for your future. These benefits are designed to offer a safety net, ensuring financial stability when you’re no longer working or facing unforeseen challenges. Navigating the system can be complex, but knowing what benefits are available and how to access them is essential.
This blog will break down the key aspects of Social Security benefits, making it easier for you to understand and utilize them effectively. Whether you’re approaching retirement, currently disabled, or planning for the future, knowing your Social Security options is vital for financial well-being.

Credit: adrccares.org
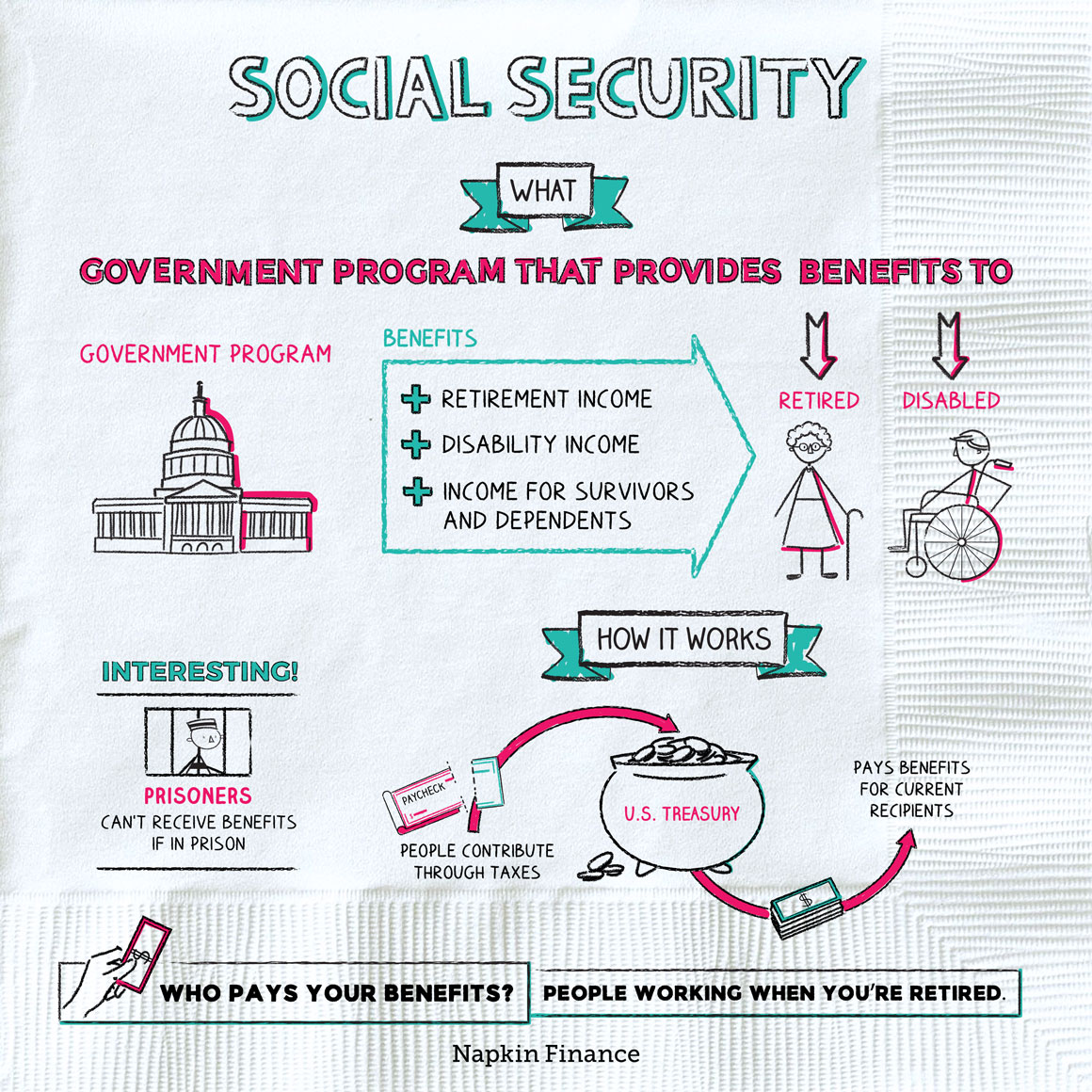
What Are Social Security Benefits
Social Security Benefits are a crucial part of financial support for many individuals and families. These benefits provide monthly payments to retired and disabled workers, their families, and survivors of deceased workers. Understanding Social Security Benefits can help you plan for the future and ensure financial stability during retirement or in the case of disability or death.
Types Of Benefits
Social Security Benefits come in various forms, each designed to meet different needs. Below are the primary types of benefits:
- Retirement Benefits: These benefits are for individuals who have retired from work. The amount you receive depends on your earnings history and the age you start collecting benefits.
- Disability Benefits: If you become disabled and cannot work, you may be eligible for disability benefits. These payments help cover daily living expenses when you are unable to earn an income.
- Survivors Benefits: These benefits are paid to family members of a deceased worker. This includes spouses, children, and sometimes parents who depended on the worker for financial support.
- Supplemental Security Income (SSI): This is for individuals with limited income and resources. It provides financial assistance to meet basic needs for food, clothing, and shelter.
The table below summarizes the types of Social Security Benefits:
| Type of Benefit | Who Can Receive It |
|---|---|
| Retirement Benefits | Retired workers and their families |
| Disability Benefits | Disabled workers and their families |
| Survivors Benefits | Families of deceased workers |
| Supplemental Security Income (SSI) | Individuals with limited income and resources |
Eligibility Criteria
Understanding the eligibility criteria for Social Security Benefits is essential. Each type of benefit has its own set of requirements:
- Retirement Benefits: You must have worked and paid Social Security taxes for at least 10 years. The age at which you start collecting benefits affects the amount you receive.
- Disability Benefits: To qualify, you need to have a medical condition that meets Social Security’s definition of disability. You must also have worked long enough and recently enough under Social Security.
- Survivors Benefits: Family members of a deceased worker may be eligible. This includes widows, widowers, and children. In some cases, dependent parents may also qualify.
- Supplemental Security Income (SSI): Eligibility is based on age, disability, and limited income and resources. You do not need to have worked to qualify for SSI.
The table below outlines the eligibility criteria for each type of benefit:
| Type of Benefit | Eligibility Criteria |
|---|---|
| Retirement Benefits | Worked and paid taxes for at least 10 years; age affects benefit amount |
| Disability Benefits | Meet the definition of disability; sufficient work history |
| Survivors Benefits | Family of deceased worker; includes spouses, children, sometimes parents |
| Supplemental Security Income (SSI) | Age, disability, limited income and resources; no work history required |
How Benefits Are Calculated
Social Security Benefits provide financial support during retirement, disability, or other life changes. Understanding how benefits are calculated is crucial for planning. The calculation involves examining your earnings over your working years and applying a specific formula. This ensures you receive a fair amount based on your contributions.
Earnings Record
Your earnings record is fundamental in determining your Social Security Benefits. The Social Security Administration (SSA) keeps track of your annual earnings. This record reflects your work history and the taxes paid into Social Security.
Here’s how the earnings record works:
- The SSA considers your highest 35 years of earnings.
- If you have fewer than 35 years, they add zeros for the missing years.
- Higher earnings result in higher benefits.
It’s essential to regularly check your earnings record. Incorrect records can lead to lower benefits. You can verify your earnings through the SSA’s online portal.
Below is a simple table illustrating how different earnings affect benefits:
| Years Worked | Total Earnings | Average Earnings |
|---|---|---|
| 35 | $1,050,000 | $30,000 |
| 30 | $900,000 | $30,000 |
| 25 | $750,000 | $30,000 |
Benefit Formula
The benefit formula is the method used to calculate your monthly Social Security payments. This formula considers your average indexed monthly earnings (AIME), which are derived from your top 35 years of earnings.
The calculation involves several steps:
- Determine your AIME.
- Apply the formula to calculate your primary insurance amount (PIA).
- PIA is the base for your monthly benefits.
The formula works in three parts, known as bend points:
- First part applies a percentage to the first portion of AIME.
- Second part applies a different percentage to the next portion.
- Third part applies another percentage to the remaining AIME.
These percentages ensure fairness across different income levels. The formula is designed to favor lower-income earners by providing a higher percentage of their average earnings as benefits.
Understanding the benefit formula helps in estimating future benefits. It also aids in financial planning for retirement.
Applying For Social Security
Social Security benefits are crucial for many individuals and families. They provide financial support during retirement, disability, or after the death of a family member. Understanding how to apply for Social Security can help you access these benefits efficiently. This guide will walk you through the application process and the required documents.
Application Process
Applying for Social Security benefits involves a few steps. It’s important to follow these steps carefully to ensure your application is processed smoothly. Here is a simple breakdown:
- Determine Your Eligibility: Check if you qualify for retirement, disability, or survivor benefits. Eligibility depends on your age, work history, and contributions to Social Security.
- Choose Your Method: Apply online, by phone, or visit a local Social Security office. Online applications are often faster and more convenient.
- Complete the Application: Provide necessary information about yourself, your work history, and your family. Be honest and accurate to avoid delays.
- Submit the Application: Once completed, submit it along with the required documents. Keep a copy for your records.
After submission, the Social Security Administration will review your application. Processing times may vary, so be patient. You can check the status of your application online or by contacting Social Security directly.
Required Documents
Gathering the right documents is essential for a successful application. These documents verify your identity and eligibility. Here’s a list of commonly required documents:
- Social Security Card: Your own or the deceased’s, if applying for survivor benefits.
- Birth Certificate: Proof of age is necessary for all types of benefits.
- Proof of U.S. Citizenship or Lawful Alien Status: Only needed if you haven’t already provided this to Social Security.
- W-2 Forms or Self-Employment Tax Returns: Provide for the past year to confirm your earnings.
- Military Discharge Papers: Required if you served before 1968.
- Spouse’s Birth and Death Certificates: For survivor benefits, if applicable.
Ensure all documents are original or certified copies. Photocopies are not accepted. Keeping these documents organized will make the application process smoother. If you are missing any documents, contact the issuing agency to obtain replacements before applying.

Credit: store.nolo.com
Claiming Benefits Early
Social Security Benefits provide financial support to retirees, disabled individuals, and families of deceased workers. Many people wonder whether they should claim these benefits early. Deciding to claim early can impact your financial future. Understanding how this choice affects your payments and considering your age is crucial.
Impact On Payments
Claiming Social Security Benefits early can reduce your monthly payments. The standard age for full benefits is 67 for those born after 1960. If you claim benefits at 62, your monthly checks will be smaller.
Here are a few key points to consider:
- Reduced Payments: Benefits claimed at 62 could be around 70% of your full benefit.
- Lifetime Impact: Smaller checks may affect your long-term financial plans.
The table below illustrates potential payment reductions:
| Age | Percentage of Full Benefit |
|---|---|
| 62 | 70% |
| 63 | 75% |
| 64 | 80% |
| 65 | 86.7% |
| 66 | 93.3% |
| 67 | 100% |
Choosing to claim early could mean less financial security in the long run. Weighing immediate needs against future stability is important.
Age Considerations
Your age plays a significant role in deciding when to claim benefits. The full retirement age is 67 for many, but claiming earlier or later can change your benefit amount.
Consider these age-related factors:
- Health Status: If you expect a shorter lifespan, taking benefits early might make sense.
- Work Plans: If you plan to keep working, delaying could increase your benefits.
- Financial Needs: Immediate financial needs may require earlier claims, despite reduced payments.
Delaying benefits until age 70 can increase your monthly payments. For each year you delay past full retirement age, benefits increase by about 8%. This delay can maximize your benefits if your health and finances allow.
Making an informed decision based on age can ensure a more secure retirement. Weigh the pros and cons carefully to find the best path for your situation.
Delayed Retirement Credits
Social Security benefits play a crucial role in retirement planning. One way to enhance these benefits is through Delayed Retirement Credits. This strategy allows individuals to increase their monthly payments by postponing the start of their benefits beyond the full retirement age. By understanding how these credits work, retirees can make informed decisions that may lead to more financial security in their later years.
Benefits Of Delaying
Choosing to delay Social Security benefits can be a wise financial move. Here are some reasons why:
- Increased Monthly Payments: For each year you delay benefits past your full retirement age, your monthly payment increases.
- Long-Term Gain: While you may receive fewer payments, the total amount over your lifetime can be greater.
- Protection Against Longevity: If you live longer, delayed credits can provide a larger financial cushion.
- Spousal Benefits: Delaying can also enhance benefits for your spouse, providing them with increased security.
The following table illustrates potential monthly benefit increases:
| Age You Start Benefits | Percentage of Increase |
|---|---|
| 66 | 100% |
| 67 | 108% |
| 68 | 116% |
| 69 | 124% |
| 70 | 132% |
How It Works
Understanding how Delayed Retirement Credits operate can help you make the best decision. Here’s a breakdown:
- Full Retirement Age: This is the age you can start receiving full Social Security benefits. It varies based on your birth year.
- Delay and Earn Credits: If you wait beyond this age, your benefits increase by a certain percentage each year, up to age 70.
- No Benefits Past 70: After reaching 70, there’s no advantage in delaying further, so it’s best to start collecting.
The increase rate is generally around 8% per year. This can make a significant difference in the total benefits received over time. Social Security Administration provides tools and calculators to help individuals estimate their benefits. Using these resources can help you plan better and maximize your retirement income.
Tax Implications
Social Security Benefits provide financial support to millions of Americans. These benefits are crucial for retirees, disabled individuals, and survivors. Yet, many recipients are unaware of the tax implications tied to these benefits. Understanding how these benefits affect your taxable income and what filing requirements you need to adhere to is essential. This knowledge can help you manage your finances better and avoid unexpected tax liabilities.
Taxable Income
Social Security Benefits might not be tax-free. Whether they are taxable depends on your combined income. This includes adjusted gross income, nontaxable interest, and half of your Social Security benefits. Here’s a simple breakdown:
- If you’re single and your combined income is below $25,000, your benefits are not taxable.
- If your income is between $25,000 and $34,000, up to 50% of your benefits may be taxable.
- Above $34,000, up to 85% of your benefits may be taxable.
- For married couples filing jointly, the thresholds are $32,000 and $44,000 respectively.
Calculating your combined income correctly is vital. This determines how much of your Social Security Benefits are taxable. Consider using IRS worksheets or consulting a tax professional for accuracy.
Filing Requirements
Knowing when and how to file is important. Not everyone receiving Social Security Benefits needs to file a tax return. Here are some key points:
- If your only income is Social Security, you might not need to file.
- Check if your combined income exceeds the taxable thresholds. If it does, filing is necessary.
- For those filing, the IRS provides specific forms and worksheets. Form 1040 or 1040-SR is commonly used.
Consider these factors:
| Filing Status | Income Threshold | Filing Necessity |
|---|---|---|
| Single | $25,000 | May need to file |
| Married Filing Jointly | $32,000 | May need to file |
Ensure you understand your filing requirements. This helps avoid penalties and ensures compliance with tax laws. Being proactive in understanding these requirements can save you time and money.
Survivor Benefits
Social Security Survivor Benefits provide financial assistance to family members after a loved one passes away. These benefits aim to ease the financial burden during difficult times. They help ensure that survivors, especially those who depended on the deceased for financial support, continue to receive income. Understanding how these benefits work can be crucial for families planning their future.
Eligibility For Survivors
Survivor Benefits are available to various family members under specific conditions. Understanding who qualifies is essential to ensure the right support is received. Here are the general eligibility criteria:
- Widows or Widowers: Eligible if they are 60 or older. If disabled, eligibility starts at 50.
- Surviving Spouse with Children: No age requirement if caring for a child under 16 or disabled.
- Unmarried Children: Eligible if they are under 18 or up to 19 if attending school full-time.
- Dependent Parents: Must be 62 or older and have relied on the deceased for support.
Other conditions may apply, such as the deceased needing to have earned enough work credits. The Social Security Administration (SSA) determines eligibility based on these credits, which depend on the deceased’s work history.
Benefit Amounts
The amount survivors receive varies based on multiple factors. Key determinants include the deceased’s earnings and the type of survivor:
- Widows or Widowers: They can receive up to 100% of the deceased’s benefit if they retire at full retirement age.
- Surviving Spouse with Children: Typically receives 75% of the deceased’s benefit.
- Children: Also receive 75% of the deceased’s benefit.
The total family benefits are subject to a limit, generally ranging from 150% to 180% of the deceased’s full benefit amount. The SSA makes adjustments to individual benefits if they exceed this limit. This ensures fair distribution among all eligible survivors.
Below is a table showing potential benefit percentages:
| Survivor | Benefit Percentage |
|---|---|
| Widow/Widower (full retirement age) | 100% |
| Surviving Spouse with Children | 75% |
| Unmarried Children | 75% |
Understanding these amounts can help families plan and secure their financial future. It’s a vital step in ensuring financial stability after losing a loved one.
Appealing Benefit Decisions
Applying for Social Security benefits can be a challenging process. Many people face denials that can be disheartening. Understanding how to appeal these decisions can make a significant difference. Whether it’s a misunderstanding or a missing document, you have the right to appeal. Knowing the reasons for denial and the steps to take can help you secure the benefits you need.
Reasons For Denial
Understanding why Social Security benefits are denied is crucial. Several common reasons can lead to a denial:
- Insufficient Work Credits: You need enough credits from work to qualify.
- Medical Condition Not Severe Enough: Your condition must significantly limit your ability to work.
- Lack of Medical Evidence: Adequate medical records are necessary to prove your disability.
- Failure to Cooperate: Not attending required exams or providing requested information can result in denial.
- Income Limitations: Earning more than the allowed limit can disqualify you.
Each case is unique, and denial reasons can vary. It’s important to carefully review the denial notice to understand the specific reasons. This knowledge can guide your next steps and inform your appeal.
Steps To Appeal
Appealing a denial involves several steps. It’s essential to act promptly and follow the right procedures:
- Request Reconsideration: Submit a written request within 60 days of receiving the denial notice.
- Gather Additional Evidence: Collect any new medical records or documentation that support your case.
- Attend a Hearing: If reconsideration is denied, request a hearing before an administrative law judge.
- Seek Representation: Consider hiring a lawyer or advocate who specializes in Social Security cases.
- Submit Written Arguments: Present a detailed explanation of why the decision should be reversed.
Being thorough and organized can enhance your chances of a successful appeal. Keeping track of deadlines and ensuring all documents are complete is vital. This meticulous approach can help you navigate the appeal process effectively.
Credit: napkinfinance.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Is It Better To Withdraw Social Security At 62 Or 67?
Deciding to withdraw Social Security at 62 or 67 depends on personal financial needs and health. Early withdrawal reduces benefits, but delaying increases them. Consider your retirement goals, life expectancy, and income needs. Consulting a financial advisor can help determine the best option for your situation.
At What Age Do You Get 100% Of Your Social Security Benefits?
You receive 100% of your Social Security benefits at full retirement age. This age ranges from 66 to 67, depending on your birth year. Check your specific age requirement on the Social Security Administration’s website for accurate details.
Who Qualifies For An Extra $144 Added To Their Social Security?
Medicare beneficiaries qualify for the extra $144 if enrolled in a plan that offers a Part B premium reduction. Check your Medicare Advantage plan for eligibility. Not all plans provide this benefit, so review the details carefully. Contact your plan provider for specific information on qualifying for the reduction.
How Much Money Do You Get From Social Security Benefits?
Social Security benefits vary based on your earnings history and age of retirement. The average monthly benefit is about $1,800, but it can range from $1,000 to $3,500. To get an accurate estimate, use the Social Security Administration’s online calculator or check your annual statement.
Conclusion
Understanding Social Security benefits is crucial for your financial planning. These benefits provide stability and support. They can significantly impact your retirement years. Stay informed about your eligibility and options. Make wise decisions to maximize your benefits. Remember to review your Social Security statements regularly.
This ensures accuracy and helps you plan better. Taking the right steps today secures your future tomorrow. Keep learning and stay proactive about your benefits. Your future self will thank you.



